Fujitsu and Inria's Jointly Develop Technology for France to Automatically Detect Anomaly AI Models
Fujitsu Limited, Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd., and Inria, the French National Digital Science and Technology Research Center, on 16th, march 2020 announced technology creation that automatically creates AI models capable of detecting anomalies in time series data taken from IoT devices and other sources.
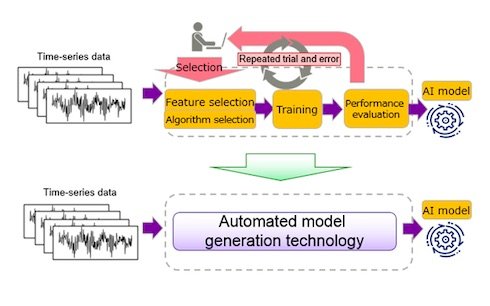
Fujitsu as AI technology has continued to progress in recent years, there has been a greater deployment of AI in a variety of business areas. Despite demand for higher levels of automation, the most common way to create AI models still involves painstaking, manual work by specialist AI engineers. Moreover, since the process of building new AI models continues to rely on trial and error, it requires significant man-hours, often leading to delays in deployment in the field.
A new jointly developed technology for automatically generating anomaly-detecting AI Models Using proprietary time series data analysis technology developed by Fujitsu Laboratories using enhanced topological data analysis (TDA)(1), Fujitsu and Inria project team DataShape have now developed a new technology for automatically generating AI models that can sense anomalies by extracting the essential information from Time series data, which can contain sensor data from IoT devices or biological data, such as heart rate and brain waves, is composed of info of a wide range of types with complex interconnections.
This means that data from the time series is also subject to extreme variability, making it difficult to determine whether there are significant trends or anomalies in the data. This technology allows any software engineer to easily construct AI categorization and anomaly detection models for time series data, while also reducing the required man-hours to one hundredth that of previous methods. This will eventually help speed up the implementation of new AI models in a variety of business fields, allowing even non-specialized engineers to build anomaly detection models.
Trials were conducted out using newly developed technologies to automatically produce models for detection of anomalies. They have shown substantial performance improvements, which will help speed up the implementation of AI models to solve real-world problems.
The newly developed technology has been integrated into GUDHI, an Inria-developed open-source TDA library, which will be available to users globally free from March 16, 2020. This will not only encourage the use of AI in businesses, research agencies, and other organizations— it will also facilitate the development of AI models for a range of use cases, as input from such organizations is reflected in ongoing technology improvements. As one of the key technologies supporting its Fujitsu Human Centric AI Zinrai suite of solutions, Fujitsu Laboratories will continue to develop this approach.
For the case of time series data that contains sensor data and biological data such as heart rate and brain waves, for example, it is often important to collect data characteristics over a variety of different time frames, and a wide range of feature types may be usable. Unless the right combination is not chosen, the model will not be able to achieve its target output, which makes it incredibly difficult to generate automatic AI models.
The Fujitsu and Inria developed technology automatically extracts the required information to establish anomaly detection models for time series data.




























